IMPACTS OF RECREATION ON FOREST ECOSYSTEMS
Project Objective
The Forest Ecosystem Monitoring Cooperative (FEMC) created tools and resources to aid managers in evaluating how increased recreational activities may be contributing to changing forest health conditions.
Overview
Forest-based recreational activities are increasing across the region, resulting in concern about pressure on recreation areas and potential impacts to the forest ecosystem. High visitor use of trail systems can contribute to excessive soil erosion, introduction and establishment of invasive plants, and disruption to wildlife behaviors and habitats. To address these impacts, FEMC partners and stakeholders identified a need for a regional assessment of the risk of impact due to recreational activities. Additionally, partners expressed an interest in resources and guidance to develop on-the-ground monitoring programs at the local level.
Process
FEMC conducted a literature review and gap analysis to identify monitoring programs and data available in the Northeast focusing on recreational impacts to forest health. Very little data was available. Following this review, interviews were conducted with experts to learn what resources and tools would be useful to land managers in evaluating and detecting impacts to forest health on recreational lands.
Products
FEMC developed two products as part of this project. Eight geospatial layers were developed to identify locations where recreational activities may pose risks to forest ecosystems. These layers incorporate visitor use data, wildlife impact buffers, and spatial environmental data and are publicly available for download to aid land managers in identifying priority management areas. A report details the analyses conducted and how the layers were created.
A decision-support tool was also created to provide managers with recommended monitoring protocols to detect impacts of recreation on the ground. The tool guides users through selecting what type of data output is of interest while also providing information about why a method should be used and any limitations to consider when implementing the method. We also provide a report describing how to implement a monitoring program, and detailing each method (with links to each of the methods included in the guidance).
Watch our recorded webinars:
- Recreation and Forest Ecosystems - Geospatial Products, presented by Soren Donisvitch
- Monitoring methods for recreation impacts, presented by Elissa Schuett
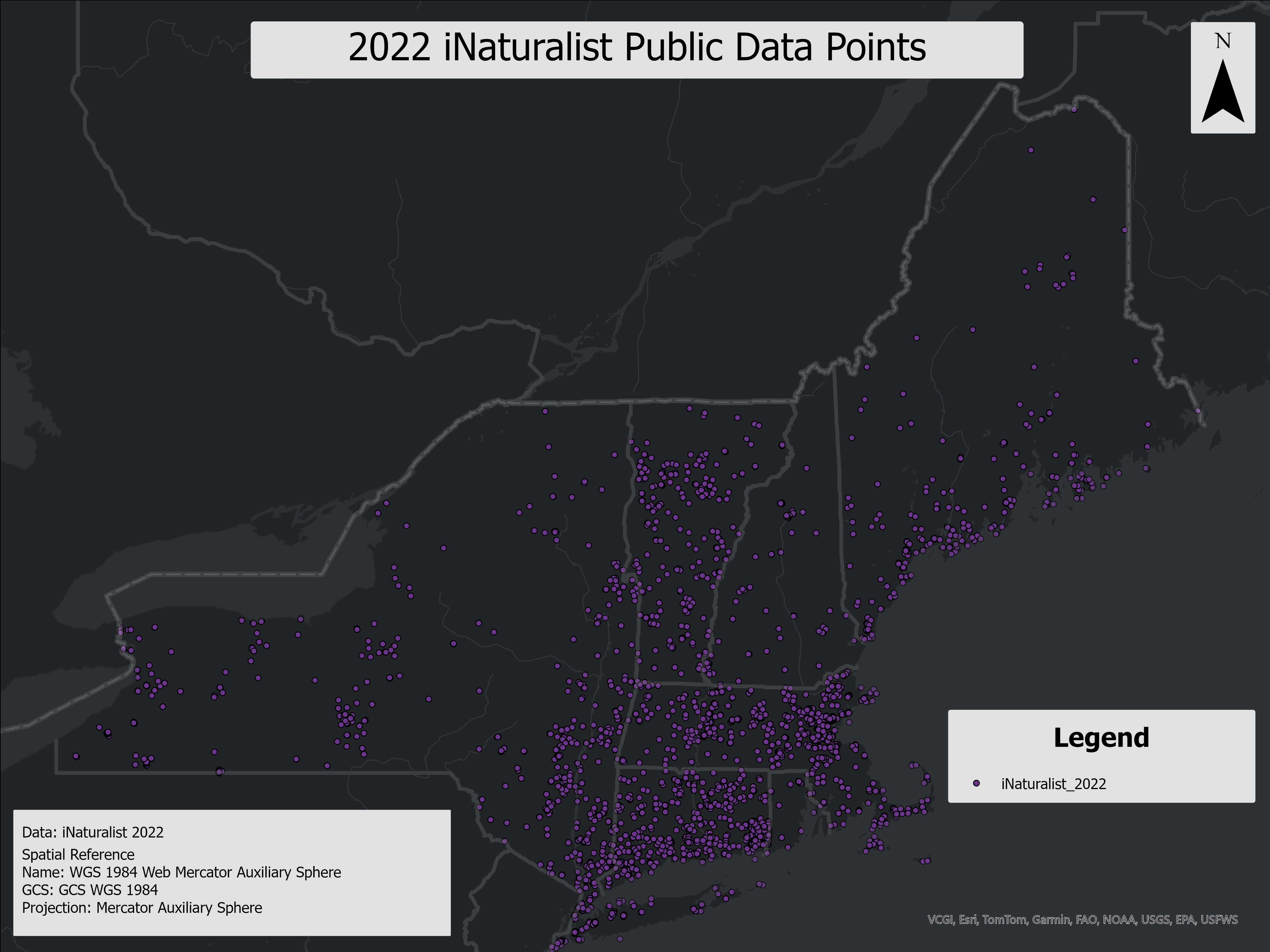
This project is centered on the analysis of recreational use, forest health, and environmental impacts within the Northeastern U.S., using various geospatial layers that combine data from OpenStreetMap (OSM), Strava, iNaturalist, and NRCS Web Soil Survey. The primary aim of the project was to identify recreational hotspots, assess the suitability of soils for sustaining such activities, and evaluate forest canopy health based on NDVI deviations from long-term baselines.
The products generated from this project include comprehensive analyses of recreational trail use, soil suitability, and wildlife impact. By integrating user-generated activity data (such as Strava and iNaturalist) with spatial environmental data (like NRCS soils and NDVI), the project provides insights into areas where recreational activity may pose risks to forest ecosystems or where management actions could be prioritized.
These layers are designed to be publicly available, ensuring that land managers, conservationists, and other stakeholders can utilize them to inform sustainable trail management, conservation efforts, and recreation planning. The datasets provide valuable tools for understanding the balance between recreational use and environmental stewardship, especially in regions where trails intersect with sensitive soils or wildlife habitats.
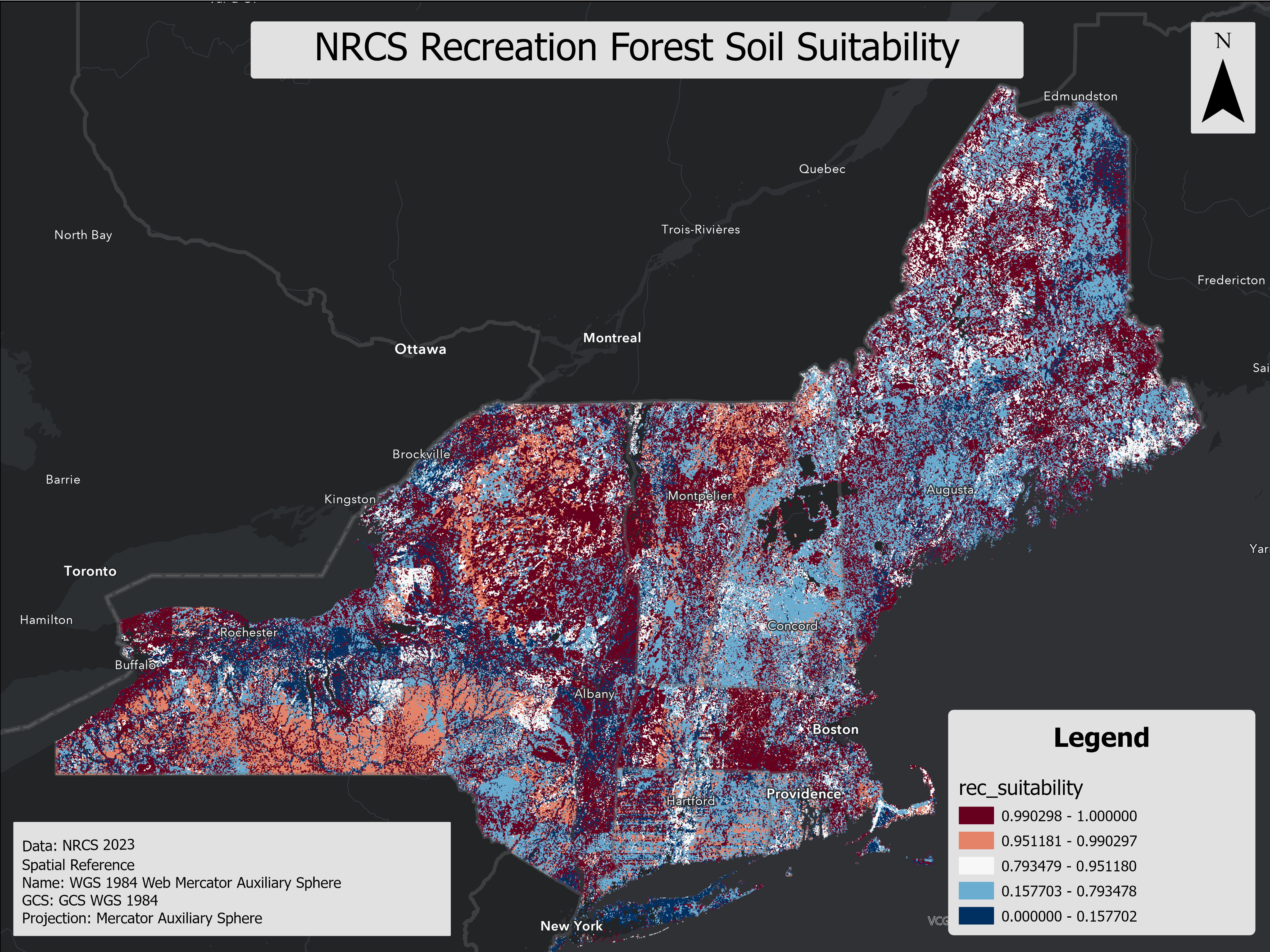
This layer evaluates soil suitability for recreational development, specifically focusing on paths and trails. It assesses key soil characteristics such as erosion potential, drainage, stone content, and load-bearing capacity to determine the feasibility of recreational infrastructure. The layer provides three interpretive ratings—Not Limited, Somewhat Limited, and Limited—based on the severity of soil-related constraints. This information aids land managers, planners, and developers in identifying appropriate areas for trail construction and managing natural resources effectively. The suitability ratings are derived from soil properties and do not account for external factors like land use, accessibility, or scenic quality.
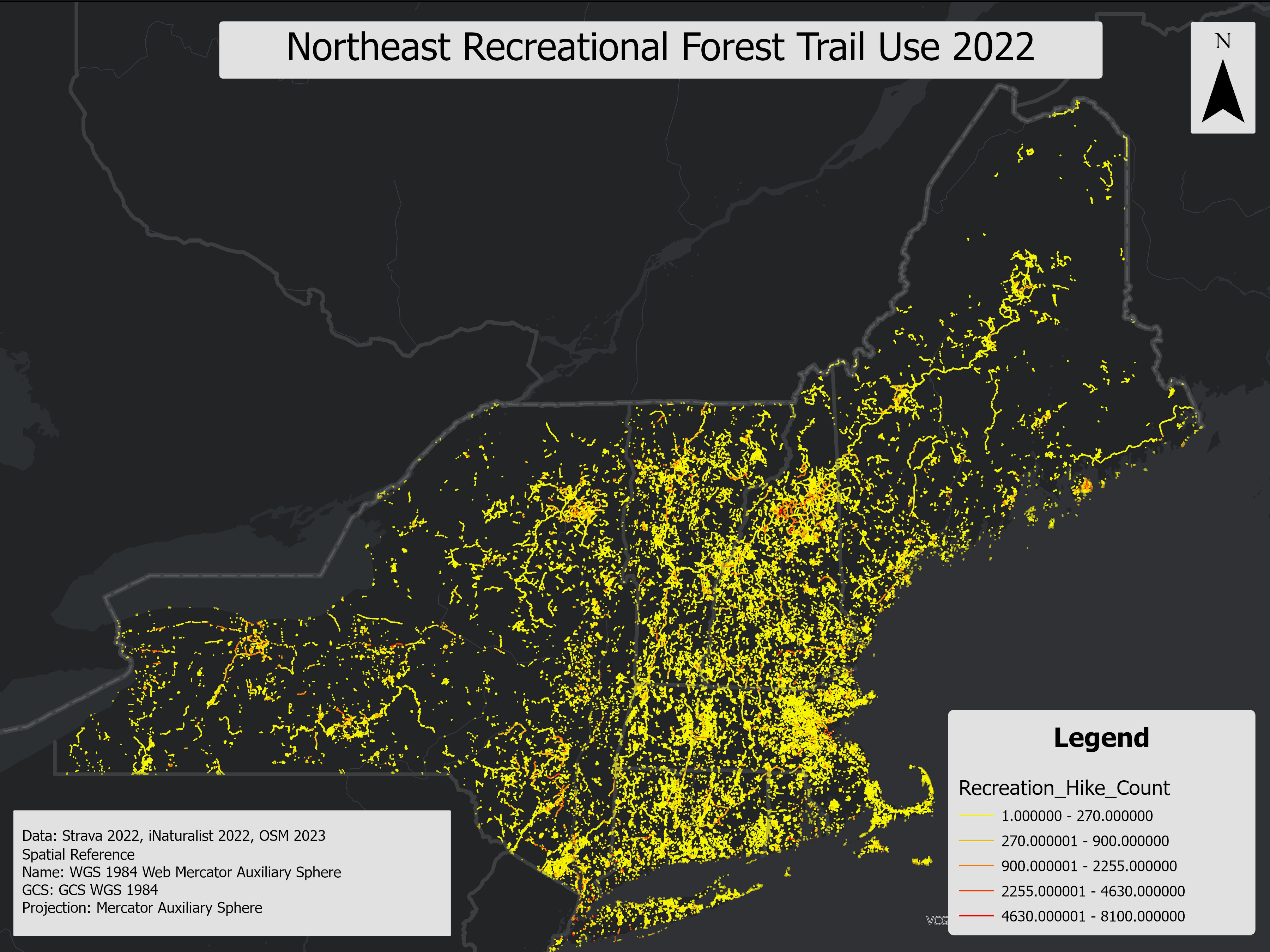
A geospatial line layer representing recreational soil use on forested permeable trials in 2022. Layer was generated using Open Street Map (OSM) ways data for permeable trails, and modeling using Strava hiking and biking use data, and NRCS web soil survey recreational modeled recreation suitability for ME, NY, NH, RI, CT, VT, and MA. The layer was clipped to the 2021 NLCD forest layer and filtered to permeable and likely permeable trails using OSM, therefore representation of only permeable trails within forested areas in the specified states.
*Release pending approval from Strava.
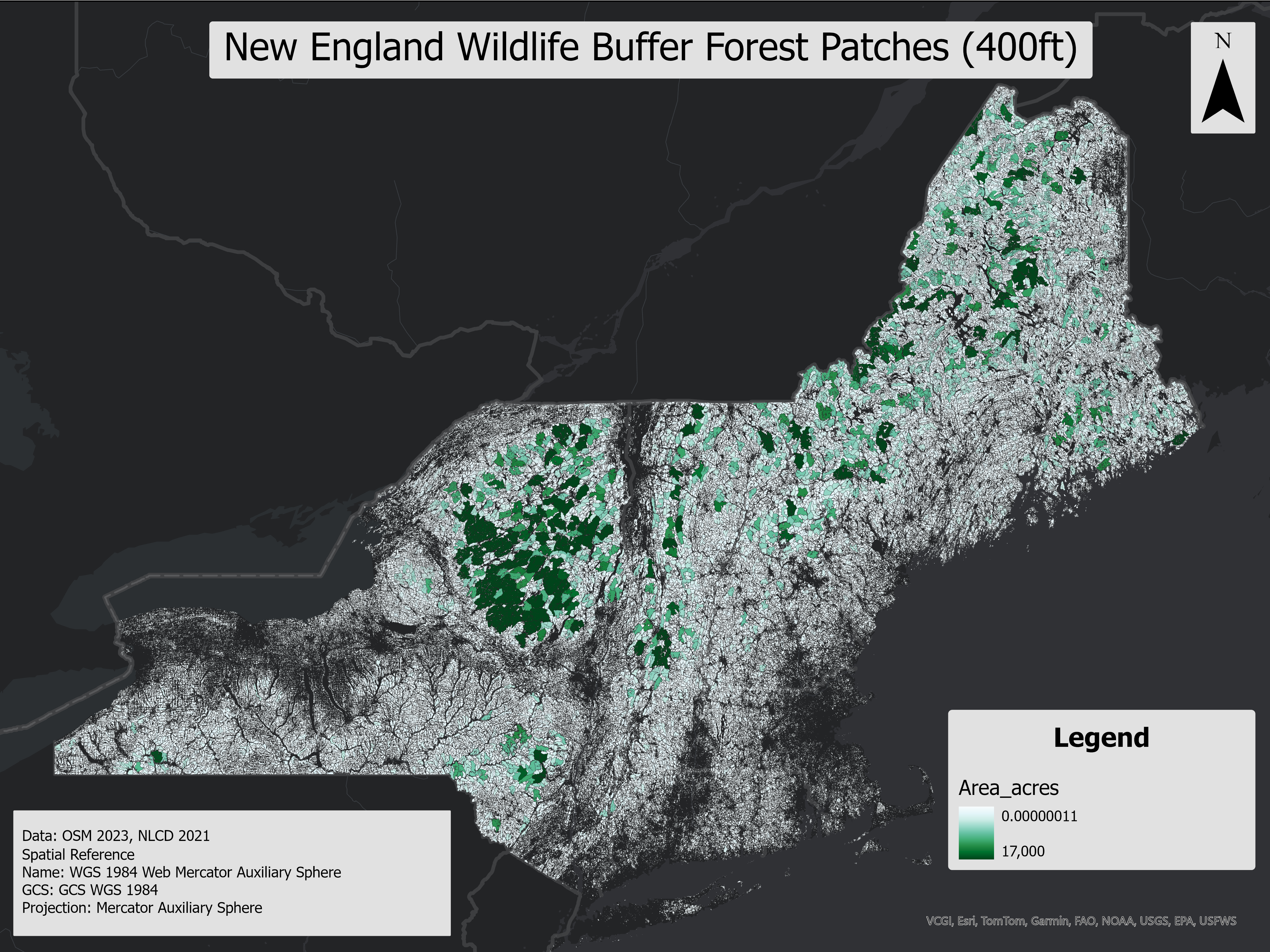
This polygon layer identifies forest patches clipped to 60 ft, 120 ft, and 400 ft buffer zones around OSM roads and trails, based on the methodology from the NH Fish and Game Trails for People and Wildlife report. These buffers represent potential zones of wildlife disturbance, with each buffer size corresponding to different wildlife species' sensitivity to human activity. Inter-connectivity between forest patches was not applied, leaving small, disjointed patches unaltered.
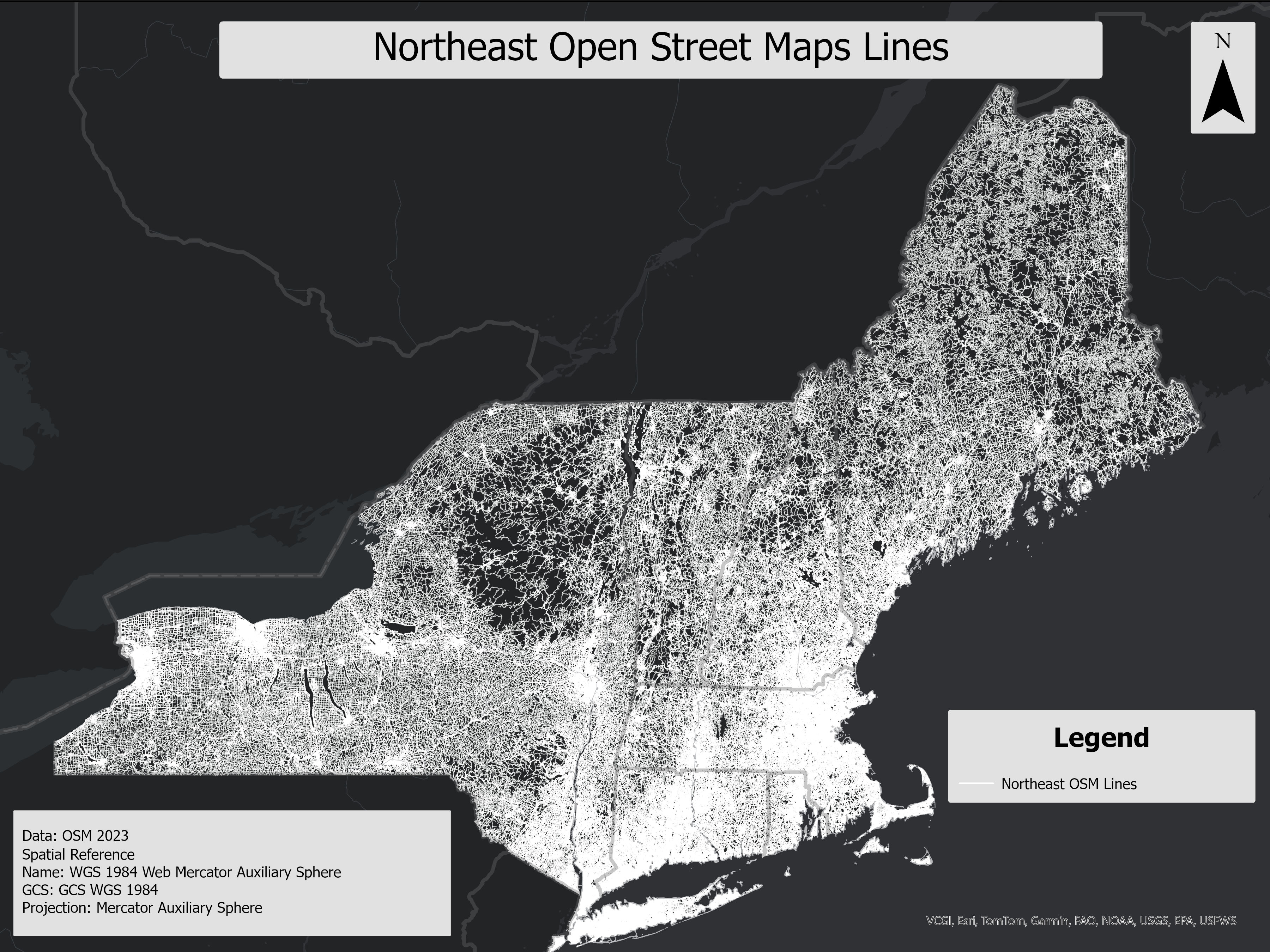
This layer contains line features from OpenStreetMap (OSM), representing various roads, trails, and paths. Key attributes include OSM ID, highway type, surface type, and shape length, making it useful for analyzing transportation networks and recreational infrastructure. The data is ideal for projects involving trail planning, infrastructure development, or environmental conservation efforts related to forest fragmentation and wildlife impact.
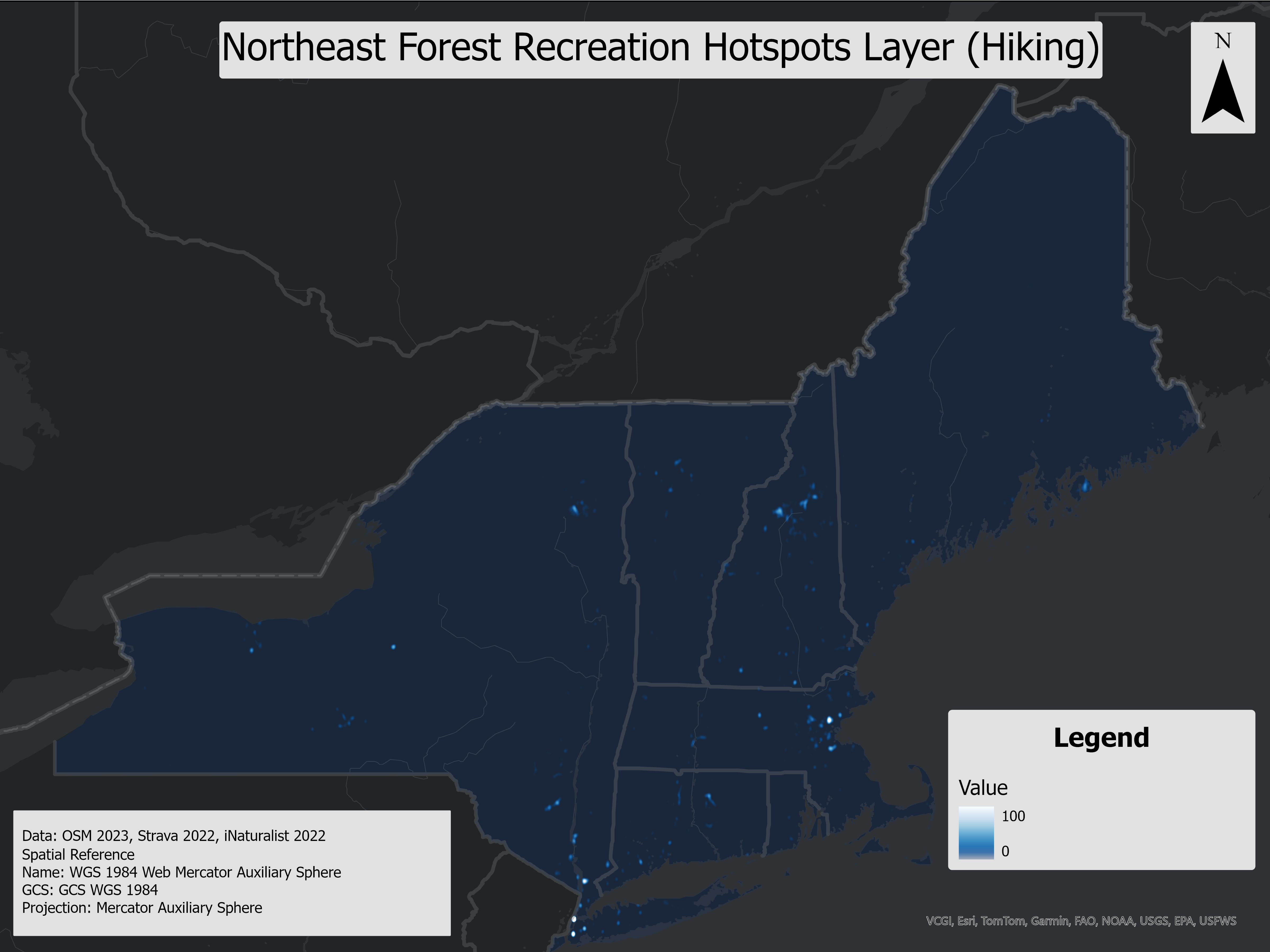
This layer represents forest recreation hotspots in the Northeast USA, derived from kernel density rasters using recreational data from Strava, iNaturalist, and OpenStreetMap (OSM) line features. It identifies high-use areas for both hiking and biking and highlights the impact of recreational activities on soil health by integrating soil recreational suitability. This analysis helps identify regions where high recreational usage coincides with poor soil conditions, providing insight into potential areas of environmental concern that might not be evident from raw recreational data alone.
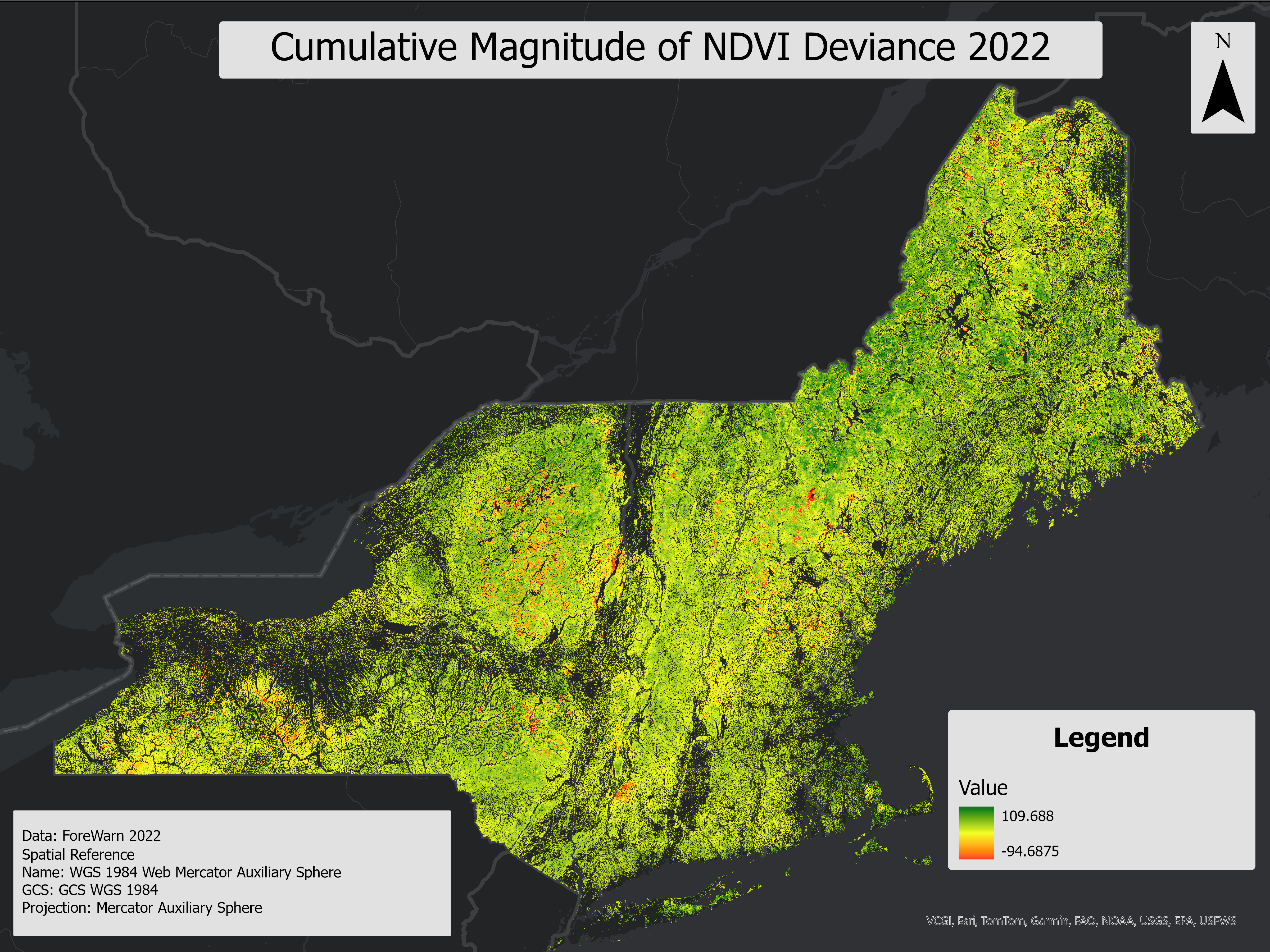
The Cumulative NDVI Deviance From Normal for 2022 growing season layer represents the maximum observed deviations in the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) over a series of time-based raster images. This layer is derived from ForWarn NDVI data and highlights areas with significant vegetation changes, providing critical insights for environmental monitoring and management.
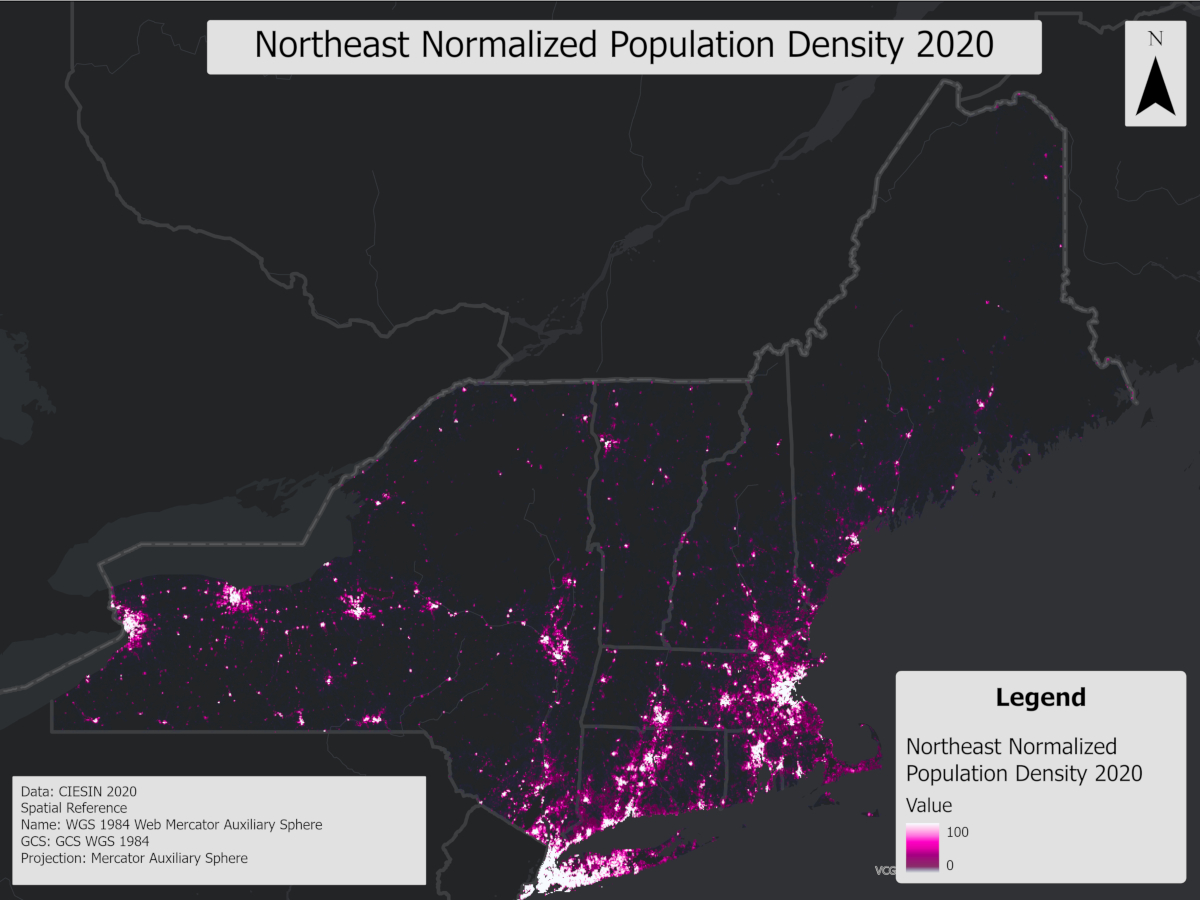
This raster represents 2020 population density from the Gridded Population of the World, Version 4 (GPWv4), clipped to the Northeast USA and normalized to a 0-100 scale. It facilitates the comparison between population distribution and recreational use in forests, helping to identify spatial outliers where recreation is disproportionate to local population.
Monitoring Methods
A wide variety of monitoring methods are available to land managers. Selecting a method that meets defined objectives is complex and requires knowing the methods available and any limitations to consider. FEMC reviewed 75 methods in three categories (soil, invasive plants, and wildlife). The methods were categorized and organized to refine the list of methods to those most to monitoring the impact of recreation in northeastern forests. Methods were selected that have been validated and have wide use, but also vary in data outputs and resource requirements. These methods can be explored using the decision support tool to help land managers select an approach that will meet their needs for detecting change in recreational areas.
Methods Decision Tree
This tool helps to identify the most appropriate experimental design for your project based on topic, data output, and available resources. Within each method description, suggestions are made on ways to adapt your experimental design to best assess impacts of recreation.
Reports
Literature Review- An exploratory literature review was conducted to assess the state of available monitoring of the impact of outdoor recreation on forest health in the Northeast. Given the increasing use of forests for recreation, this search supported the need to identify options for monitoring aspects of forest health that interact with recreational uses. Academic databases were initially searched for articles assessing the effects of specific recreation types (i.e., hiking, mountain biking, camping) and outdoor recreation in general.
Recreation Expert Interview Report- To support the study exploring impacts to forest health from outdoor recreation, regional experts and stakeholders were interviewed to identify ongoing monitoring efforts and key questions for future research. Fifteen individuals were interviewed from states in the region, including Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, New York, Rhode Island, and Connecticut. Although there is concern for the impact recreational uses have on the health of eastern forests, efforts to monitor these impacts are not typically being pursued. This is primarily due to a lack of funding, staffing, or large forested areas to monitor. Regional stakeholders and land managers are interested in future projects that provide direct recommendations, transferrable results, and a community with shared values to work with.
Geospatial products technical report- This project investigated the impact of recreational hiking and biking on forest health. The analysis utilized several geospatial data sources, including ForWarn Sentinel data (ForWarn, 2022), Strava recreational use data (Strava, 2023), iNaturalist identification location information (iNaturalist, 2024), NLCD forest data (NLCD 2021), and USDA soil survey data (NRCS, 2023). The primary objectives were to determine whether forest-based recreational use correlates with forest tree canopy health and to provide managers with tools to help identify areas where soils are more susceptible to recreational use and where recreational activities may disturb wildlife.
Monitoring Methods Decision Support Guide- To aid forest managers in identifying and measuring impacts, FEMC developed a methods selection decision support tool and this resource guide. This guide provides background information about ways in which the forest may be affected, focusing on soil erosion, invasive plant introduction and expansion, and wildlife behavior and habitat disturbance. We reviewed a range of monitoring methods for each focus area, summarizing their key features and outlining the limitations of each. We also identified scenarios in which a given method would be most appropriate for addressing the questions of interest. The methods were selected based on a variety of factors including validity and history of successful implementation in Northeastern forests, ease of use, robustness of data output, and ability to compare across sites and datasets.
Webinars
Recreation and Forest Ecosystems - Geospatial Products, presented by Soren Donisvitch
Monitoring methods for recreation impacts, presented by Elissa Schuett
Project Quick Facts
Start Date:
1/1/2022
End Date:
12/31/2024